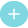
Bird Banding in Canada
- began centuries ago, mainly as a way to identify hawks used in falconry and homing pigeons
- has been an active program in Canada since 1923
- provides data that leads to important habitat protection measures, such as establishment of the Western Hemispheric Shorebird Reserves in 1986
- in Canada currently involves more than 900 authorized banders placing identifying markers on over 300 000 birds from about 300 species each year
How is banding done?
Bird banding is one of the most useful tools in the study of wild birds. Wild birds are captured and marked, usually with a numbered metal band placed on the leg. The bander records information about the bird, as well as where and when it was banded.
Data from recovered bands provide information on the distribution and movement of species, their relative numbers, annual production, life span, and causes of death. Such information increases our knowledge and understanding of birds and their habits and helps us to manage and conserve them.
Birds can be banded at any age provided their feet are large enough to prevent the loss of bands. Young may be caught by hand at the nest before they can fly. Adults are usually caught in traps or nests.
Many different types of traps have been devised to capture birds as safely as possible. Traps set up at baited bird feeders, or at nest sites when the birds are incubating, or sitting on eggs, are particularly successful. The design and construction of such traps are described further in North American Bird Banding Techniques, Volume II (Canadian Wildlife Service et al. 1977).
A common method for catching songbirds involves a “mist net.” A fine nylon net is stretched between poles across an area where birds are likely to fly. When a bird flies into the net it becomes entangled; it is unharmed but cannot escape. The bander regularly patrols the nets, collecting and banding the catch. This method requires considerable experience and skill to capture large birds without harming them.
Cannon nets are also used to catch birds feeding or resting in close groups. Bait is set out to attract the birds to the site where the nets have been set up. Then small rockets attached to the nets are fired, throwing the net over the feeding birds.
The bander must identify the bird by species as well as by age and sex before applying the band. About 645 species of birds breed north of Mexico on this continent and most are easily recognized with some practice. Identification of a bird’s age and sex is usually more difficult, however. Various criteria are used depending on the species and time of year.
Banders examine the shape, colour, and texture of feathers, colour of bill, colour of mouth or eyes, stage and type of plumage moult, or feather replacement, and amount of bone growth in the skull. In addition, the presence of a featherless area on the abdomen of some birds or a cloacal protuberance—a swelling developed by sexually active males—may distinguish the age and sex of birds during the breeding season.
Before the band is applied, its number is recorded with the date, location, and species of the bird. The bird’s age and sex are recorded, if possible.
Banders often record other information useful to their particular project, such as size of fat deposits, number and type of parasites, measurement of body parts, or extent of moult.
The size and design of bird bands vary according to the species being studied. The band must be large enough that it does not constrict the bird’s leg, yet small enough that it will not slip off or hinder the bird’s activities. Hummingbird bands are so tiny that each one must be cut and shaped for the individual bird.
Large birds of prey, such as hawks and eagles, need special lock-on or rivet bands because their strong beaks can easily rip off the simple aluminum butt-end bands used on most birds.
The band is applied by carefully squeezing it closed around the lower part of the leg with a pair of pliers. The band is inscribed with a message such as “Call 1-800-327-BAND” or “Write Bird Band Laurel, MD 20708 USA,” plus a unique eight- or nine-digit number.
Other marking devices, such as neck collars, plastic streamers, wing tags or nasal saddles, feather clipping, and paints or dyes, can be used in addition to the standard metal bands. Coloured plastic leg bands are the most common auxiliary markers. These are usually coded to allow individual birds to be recognized without recapturing them.
More than 300 000 birds are now banded annually in Canada by more than 900 authorized banders. Of the approximately 518 species of birds occurring in Canada, about 300 species are banded each year.
Slightly more than half the birds banded in Canada are game birds banded by government agencies; the rest are non-game species such as songbirds.
Who is responsible?
When systematic banding began in North America in the early 1900s, many organizations were involved, with little coordination of their efforts. The public was largely unaware of banding and its uses, and as a result, many bands were not returned to the bander. At the same time, conservationists were becoming aware of the need for a continental plan for conserving and managing migratory birds. Market hunting was becoming excessive and many species were threatened.
Public concern for the fate of the Passenger Pigeon, declining stocks of waterfowl, and overshooting of egrets for their plumes culminated in an international agreement to manage migratory birds. In 1916 the Migratory Birds Convention was signed by Britain, on behalf of Canada, and the United States. The convention set out a system of protection for migratory birds and regulated the killing of the birds in both countries. In 1936, when the United States signed a treaty with Mexico, that protection was extended to cover all North America.
Government agencies that were given the responsibility of administering the convention also coordinated banding efforts on the continent. The Canadian Bird Banding Office was established in 1923 to issue permits, supply bands, and keep records of Canadian banding activities. It is now administered by the Canadian Wildlife Service (CWS), Environment Canada, in Ottawa. In the United States, the U.S. Bureau of Biological Survey—now the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service—was established in 1920 with similar responsibilities, and the Bird Banding Laboratory in Washington, D.C., became the centre for American banding activities.
Close coordination is maintained between the two offices, and identical bands, with different band numbers, are used in both countries. Central files in Washington, D.C., contain the data for all birds banded in North America.
Recovering bird bands
If you find a bird band, it is important to gather all the information you can about the bird and return the band, with the information, to the Canadian Bird Banding Office, Canadian Wildlife Service, Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0H3.
Flatten the band and tape it securely to a piece of paper. On the paper clearly print your name and address, the date the band was found, the location as exactly as possible (distance and direction from the nearest town), the species (plus age and sex of the bird, if possible), and how the bird was found or killed.
If the banded bird is alive, do not remove the band; record all the information that you can and release the bird.
On receipt of your recovery report, the Bird Banding Office will send you a Certificate of Appreciation, telling you where the bird was banded, by whom, and what kind of bird it was. The bander will be told where and when you found the band.
In Canada, about 10 percent of bands applied to game birds and less than one percent of those applied to non-game species are recovered.
What we learn
Bird banding data are useful to both researchers and managers. Individual identification of birds makes possible studies of dispersal and migration, behaviour and social structure, life span and survival rate, reproductive success, and population growth.
Many studies have been made of the movements of birds. Late each summer, thousands of ducks and geese are banded on their breeding grounds in Canada. Band returns during the hunting season in autumn trace the path of their southward flight to their wintering grounds. Information on the movements, numbers, and survival of waterfowl, collected using banding, affects the setting of hunting regulations.
The establishment of the Western Hemispheric Shorebird Reserves, which protect habitat crucial to shorebirds in Canada, the United States, and Latin America, began in 1986 on the basis of information from banding. Banding is also being used as a tool to monitor the effects of deforestation on birds that spend the non-breeding season in Latin America and migrate to Canada to breed.
The Canadian system
Any project involving the use of bands or the marking of migratory birds requires a federal banding permit, which is available from the Canadian Wildlife Service, Ottawa K1A 0H3. Additional permits from the provincial wildlife agencies may be required for provincially protected birds, such as hawks and owls.
Persons applying for a bird banding permit in Canada must be at least 18 years old. Two qualified ornithologists or persons who hold active banding permits must verify that the applicant can capture and handle birds without harming them, can identify them, and can keep accurate and detailed records. Prospective banders are also required to submit a description of their banding project.
CWS bands and permits are not needed for non-migratory game birds (grouse, partridge, quail, ptarmigan, prairie chickens, pheasants, and turkeys). Privately held avicultural, or raised, birds, such as pigeons, whether federally protected, domestic, or pet stock, carry private bands.
Information on bandings and recoveries of birds is sent to the Canadian Bird Banding Office. The data are available to the public on request. Records are available for game birds banded in North America from 1908 to the present, and for non-game birds from 1955 to the present.
Resources
Online resources
American Ornithologists’ Union
Association of Field Ornithologists (formerly Northeastern Bird-Banding Association)
The Eastern Bird Banding Association
The North American Banding Council
Ontario Bird Banding Association
Ottawa Field-Naturalists’ Club
The Western Bird Banding Association
Print resources
The Auk. American Ornithologists’ Union.
The Canadian Field-Naturalist.
The Condor. Cooper Ornithological Society.
Journal of Field Ornithology (formerly Bird-Banding). Association of Field Ornithologists (formerly Northeastern Bird-Banding Association)
The Journal of Wildlife Management. The Wildlife Society.
North American Bird Bander. Eastern and Western Bird Banding Associations.
Ontario Bird Banding. Ontario Bird Banding Association.
Ottawa Field-Naturalists’ Club.
The Wilson Bulletin. Wilson Ornithological Society.
© Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, represented by the Minister of the Environment, 1981, 1982, 1993. All rights reserved.
Catalogue number CW66-53/1992E
ISBN 0-662-19390-3
Text: C. Hyslop
Revision: E. Hayakawa, 1990
Photos: Canadian Wildlife Service